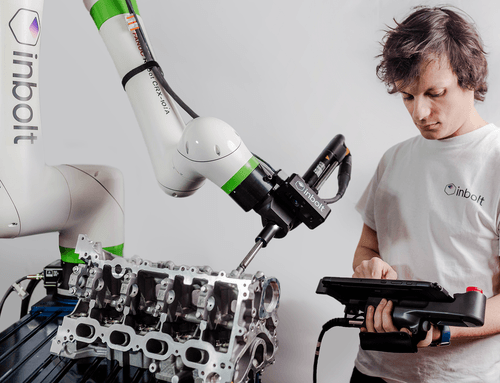
The Skills Needed for Tomorrow’s Industry
Tomorrow’s industries require ever-changing skills, particularly as automation advances. We’re taking a look at these changes and the evolution currently happening in the manufacturing industry.
Preparing for Tomorrow’s Industry: The Evolution of Skills
The pace at which industries are progressing, technologically speaking, combined with the growing labor shortage, means that the manufacturing industry is currently undergoing dramatic shifts, which will require dramatic changes to overcome.
Trends in automation are pointing to faster job growth for designing and building robots, as well as for programming the software that runs them. McKinsey & Company estimates that as many as half of the activities carried out by workers could be automated, with an annual global economic impact of $4.5 trillion for advanced robotics and up to $2 trillion for autonomous vehicles.
Robots play a big part in the day-to-day work in many industries and are poised to play an even greater role as technology advances and robots are able to move faster, have conversations, and complete increasingly complex tasks.
IFR members estimate that over 50% of production operators will be working with robots in 10 years’ time. These changes mean roboticists are in demand and will become ever more so in the coming years.
As more of these cases arise, the industry needs to adapt.
As goes the old adage, “Every challenge brings an opportunity.”
Notably, the manufacturing domain is on the brink of a transformative phase due to an increase in automation and robotics. A clear indicator is the anticipation that robots could potentially handle up to half of the tasks currently managed by human workers. In practical terms, warehouse workers, who traditionally managed heavy lifting, are now overseeing robots executing the same task. This not only increases efficiency but also promotes workplace safety, resulting in reduced healthcare and insurance costs.
The integration of robotics in various industries isn’t just a trend; it’s a future reality. The International Federation of Robotics predicts that over half of production operators will be collaborating with robots within a decade.
Given this trajectory, several key areas demand our attention:
1. The Increasing Demand for Robotic Operation Skills
As the manufacturing industry starts to lean more and more into automation, robots of all shapes and functions have started to emerge in a lot of sectors.
Robots by design are faster and more efficient—if programmed correctly. However, this transition from human to machine demands not only people who can work alongside robots, but individuals who are proficient in operating, maintaining, and innovating with these machines as well.
In this evolving landscape, several key skill sets have become paramount:
- Robotic Programming, which requires a deep understanding of coding and programming languages specific to robots.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting, which equip people with the ability to diagnose issues and carry out essential maintenance.
- Collaborative Robot Operation to ensure people can handle robots designed to work alongside humans.
2. The Emergence of Specialized Training Platforms
Everyone involved in making robots and using them, like robot makers, employers, schools, unions, and government, should all work together to make sure workers get the help they need to avoid losing skilled workers in the future. Mike Cicco, the CEO of FANUC America, explained, ‘Unless we prepare the manufacturing industry for the factory worker of the future, we’ll lose skilled labor, which is already reduced due to demographic change’.
Recognizing this urgent requirement, various institutions—both public and private—have been establishing programs focused on transmitting these needed skills.
Universities: More universities are now incorporating robotic courses into their curriculum, ensuring students are industry-ready from the get-go. From basic introductory courses to advanced degrees in robotic engineering, the academic sector is rising to meet the demand.
Poland, for example, has encouraged students to study science, leading to more students in college studying science-related subjects. There are also special programs, like the First Robotics, which introduce school kids to robotics through fun competitions.
Public/private technical centers: Highlighting the collaborative efforts between public and private sectors, Proxinnov in France stands as a shining example. Serving as a public-private technical center, it specializes in industrial robotics tailored for SMEs (PME) and medium-sized enterprises (ETI). Operating out of La Roche sur Yon, their dedicated team of 11 experts uses cutting-edge robotic equipment to drive innovation and support various robotic projects. These centers aren’t just training hubs; they’re innovation incubators that provide industrials who have theoretical knowledge with practical, hands-on experience.
3. The Way Forward
Manufacturing is the backbone of many economies and has an important role in generating jobs in related service industries.
As companies plan for their future workforce, they can focus on a few actions to evolve, with the two main ones being:
- Retraining: improving the skills of current staff and training new employees to preserve in-house knowledge.
- Redeployment: optimizing existing skills by reorganizing job tasks or redesigning processes.
Automation is profoundly altering the face of manufacturing, creating promising new opportunities for employees at all skill levels. It’s an exciting future, for both new and existing workers, but a future whose potential will not be realized unless urgent action is taken to address an existing and future skills gap.
4. New Robots
New collaborative robots (cobots), are also flooding the market and enhancing the native abilities of human workers. Ranging in size from two to four feet high, these automated assistants work with humans to perform tasks that perhaps are slightly dangerous or repetitive, or that require special agility to work in tight or hard-to-reach places. For instance, Renault has deployed cobots in a few plants to help build the powertrain—torquing bolts to a certain tolerance, a task that can be tedious for humans to do consistently and efficiently.
Tomorrow’s industry will be characterized by harmony between humans and robots. While this may sound like the premise of a sci-fi novel, it’s our reality. Embracing the necessary skills today will ensure that we’re not just prepared, but are pioneers in this exciting new world.
Explore more from Inbolt
Access similar articles, use cases, and resources to see how Inbolt drives intelligent automation worldwide.
Reliable 3D Tracking in Any Lighting Condition

The Circular Factory - How Physical AI Is Enabling Sustainable Manufacturing
NVIDIA & UR join forces with Inbolt for intelligent automation
KUKA robots just got eyes: Inbolt integration is here

Albane Dersy named one of “10 women shaping the future of robotics in 2025”

Want to Sound Smart About Vision‑Guidance for Robots?

Inbolt Joins NVIDIA Inception to Accelerate AI-Driven Automation